Cloud Service Models
The Evolution of IT: From On-Premises to the Cloud
Introduction
Cloud computing provides many online technology usage and management options for enterprises.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the three categories of cloud services.
There are variations in the control and administration of IT resources offered by each service model.
Knowing these models makes it easier for enterprises to select the best one for their requirements, whether they are handling infrastructure, managing software, or developing applications.
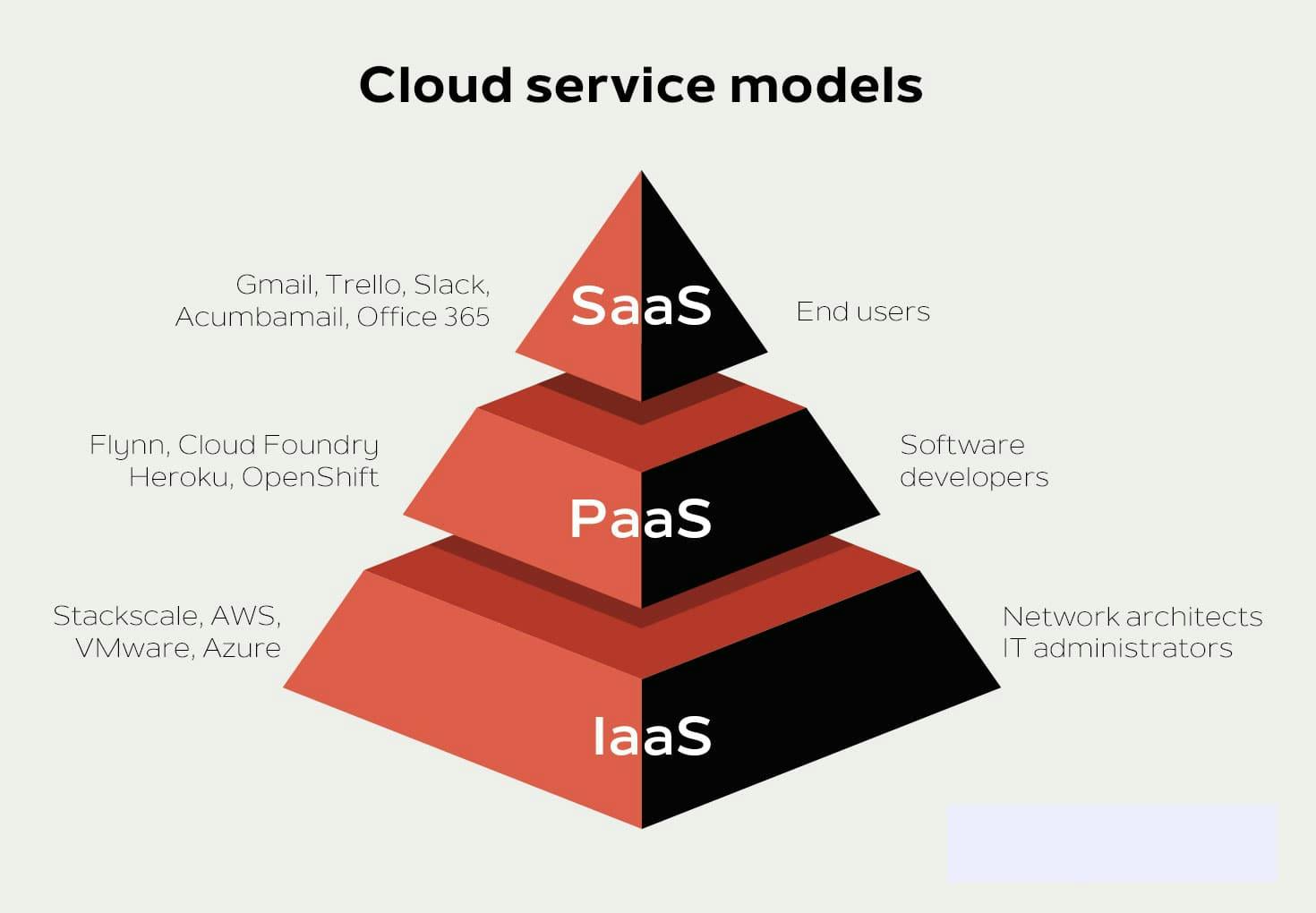
Types of Cloud Service Models
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is comparable to online computer, storage, and networking equipment rentals. You can use virtual resources offered by a cloud service provider in place of purchasing and maintaining real hardware.
The operating systems, apps, and software that are installed on these virtual machines are under your control, and the actual infrastructure is handled by the cloud provider.
How does IaaS Work?
Using a web portal or an API, you can access virtualized resources via the internet (Application Programming Interface).
Based on your demands, you can select the kind and quantity of networking, storage, and virtual machines (VMs).
In order to guarantee dependability and security, the cloud provider maintains the hardware, which includes servers, storage devices, and networking equipment.
Benefits of IaaS
The need to purchase and maintain physical hardware is eliminated when resources may be easily scaled up or down in response to demand.
You have complete control over your environment since you can install and configure any program or operating system on your virtual computers.
There are no up-front expenses for hardware or infrastructure maintenance—you simply pay for the resources you utilize.

Example
Assume you are a newly formed business introducing a brand-new online application. You can utilize Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) from a provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) in place of purchasing servers and networking equipment.
Using EC2, you may host your web application rapidly by deploying virtual servers with various configurations. Without having to worry about maintaining actual hardware, you can scale your infrastructure to accommodate an increasing user base.
For instance, you may quickly add extra virtual servers to manage an unexpected spike in traffic to your application and then scale back during slower periods to save money.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
You don't have to bother about purchasing furniture, appliances, or décor when you rent a furnished apartment. In the same way, PaaS relieves you of the burden of configuring servers, databases, and other infrastructure elements.
Similar to moving into a fully furnished apartment, developers may instantly begin building and delivering apps with PaaS by utilizing the development tools and services that are made available to them.
The building's infrastructure is maintained by the landlord (cloud provider), and tenants (developers) concentrate on making their living quarters comfortable (building applications) (PaaS platform).
That is to say, you get a platform that takes care of the underlying infrastructure and offers services and tools for creating, deploying, and maintaining applications.
The ability to handle servers, databases, and networking resources frees developers to concentrate on writing code and creating applications.
How Does PaaS Work?
PaaS platforms enable the creation of applications by providing hosting environments, databases, middleware, and development tools.
To create, test, and launch apps, developers can use the command-line interface (CLI) or web browser to access these tools and services.
Developers are free to concentrate just on developing code because the cloud provider handles all underlying infrastructure management, including servers, storage, networking, and security.
Benefits of PaaS
PaaS reduces the time needed to develop and launch apps by offering ready-to-use development tools and services. This speeds up the development process.
Applications may manage varying workloads without the need for user intervention thanks to PaaS systems autonomous scaling capabilities.
You just pay for the services and resources you really utilize; hardware and infrastructure don't need to be purchased or maintained.
Example
Assume you are a developer developing a fresh web application. You can utilize AWS Elastic Beanstalk in place of installing servers, configuring databases, and managing networking resources.
You may concentrate on building code in your favorite programming language (Java,.NET, Node.js, Python, or Ruby) and easily publishing it to the platform with AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Your application deployment, scaling, and management are taken care of by Elastic Beanstalk, freeing you up to focus on developing features and improving user experience.
Elastic Beanstalk, for example, automatically scales your application by adding more resources to handle the load, without requiring manual intervention, if you need to accommodate higher traffic.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is similar to purchasing DVDs or downloading episodes of your favorite TV shows instead of subscribing to a streaming service. SaaS eliminates the requirement for local software installation and maintenance by allowing you to access software programs over the internet on a subscription basis.
Users can use a mobile app or web browser to access the software, and the provider handles all updates and maintenance.

How Does SaaS Work?
SaaS companies let users access their software through the internet, hosting and maintaining it on their servers.
Customers pay a recurring price, usually monthly or annually, for the service, which varies according to the features and use levels they need.
The supplier takes care of infrastructure maintenance, data backups, security patching, and software updates so that customers always have access to the most recent version of the program.
Benefits of SaaS
Installing or updating software is not necessary for users to access SaaS applications on any device, from any location with an internet connection.
SaaS apps don't need extra hardware or infrastructure investments to scale to meet expanding user bases or higher consumption.
SaaS does not need customers to pay for hardware upfront or for software license; instead, it operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where users only pay for the capabilities and resources they actually use.
Example
Assume you are employed by a small company that requires its staff to have access to email, document collaboration, and video conferencing capabilities.
You can utilize Google Workspace in place of configuring email servers and installing productivity apps on each worker's PC.
Gmail: Workers have access to business email addresses with lots of storage, spam filtering, and adjustable preferences.
Google Drive: Together with version control and cloud storage for convenient access from any device, team members may work together in real-time on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
Google Meet: Google Meet provides HD video and audio quality, screen sharing, and interaction with other Google Workspace products for remote meetings and video conferencing.
Google Calendar: For improved collaboration, staff members can set up meetings, activities, and appointments with shared calendars and automated reminders.
Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides: Strong online editors with integrated collaborative tools for generating and modifying documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
Conclusion
Cloud computing offers many online technology usage and management options for enterprises.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the three primary categories of cloud services.
The level of management and control over IT resources vary depending on the kind of service.
Businesses can select the best solution for their needs, such as developing apps, handling software, or managing infrastructure, by being aware of these offerings.
IaaS is similar to renting computers and other hardware online as instead of purchasing and maintaining them yourself.
PaaS provides the resources and services needed to create and execute applications without having to worry about the backend.
SaaS enables users to utilize software via the internet in place of installing and maintaining it locally.
Selecting the appropriate solution can improve productivity and result in long-term cost savings for firms.
