Introduction
AWS began providing web services now known as cloud computing for IT services back in 2006.
We no longer need to worry about pre-purchasing servers or other IT equipment thanks to cloud computing.
As an alternative, we can easily obtain thousands or even hundreds of servers as needed.
AWS is less expensive since we just pay for what we use there are no up-front fees or longer contracts.
Today, many companies across 190 countries rely on AWS as a dependable, scalable, and reasonably priced cloud platform.
It's well-liked since it conforms to the most recent developments in digital technology.
Numerous services, such as computation and storage, are provided by AWS.
It offers several services, such as:
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) : It provides you with minimal computational power.
Platform as a service (PaaS) : It provides an environment for creating and managing software.
Software as a service (SaaS) : It offers software packages that are ready to use.
Advantages of AWS
Easy Growth : As your demands change, you may simply modify your resources to keep your system operating efficiently.
Saves Money : Since you only pay for what you use, you can avoid large upfront expenses and make long-term financial savings.
Reliable Service : Your apps are always accessible when you need them since AWS is designed to run continuously.
Keeps Things Safe : Strong security protections are in place on AWS to protect your apps and data from threats and hackers.
Always Improving : AWS is always releasing new capabilities, so you can experiment with new ideas and keep your tech up to current without any difficulties.
History & Evolution of AWS
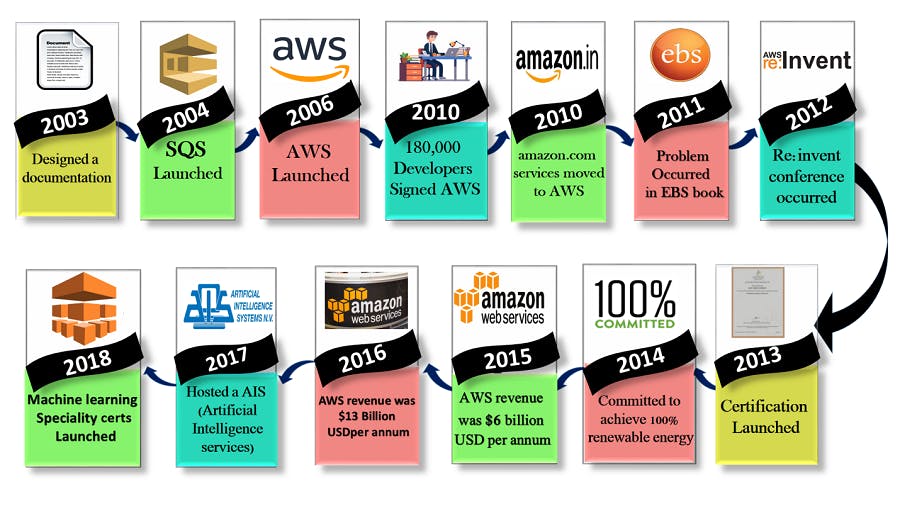
2003 : Amazon's internal infrastructure was proposed to be sold as a service by Chris Pinkham and Benjamin Black. They created a six-page document, which they reviewed before deciding to proceed with the proposal.
2004 : In Cape Town, South Africa, Amazon formally released Simple Queue Service (SQS) through a team of presenters.
2006 : Amazon introduced AWS as a platform for web services, beginning with basic computing and storage services (EC2) and storage services (S3).
2007 : AWS has almost 180,000 developers registered, demonstrating the developer community's quick recognize and appreciation of the platform.
2010 : The migration of Amazon.com's retail online services to AWS showcased the scalability and dependability of the infrastructure.
2011 : AWS encountered significant technical challenges, including as Elastic Block Store (EBS) volume issues and service interruptions that impacted well-known websites like Reddit and Pinterest.
2012 : At the re:Invent conference, AWS held its first customer event where new goods and services were introduced. But the platform also had technical issues that affected a number of well-known websites.
2013 : AWS added to its reputation and industry knowledge by introducing certifications for cloud computing-focused software engineers.
2014 : In an effort to show its dedication to the environment, AWS pledged to use only renewable energy for all of its global operations.
2015 : AWS's yearly sales topped $6 billion, growing at a speed of 90% annually.
2016 : AWS's sales doubled to $13 billion yearly, demonstrating its supremacy in the cloud computing sector and ongoing growth.
2017 : Businesses adopted AI capabilities, and as a result, revenue doubled to $27 billion yearly after AWS re:Invent showcased a variety of AI services.
2018 : In order to further establish itself as an industry leader in cutting-edge technology, AWS introduced Machine Learning Specialty Certifications, which are focused on automating AI and machine learning procedures.
2020 : In order to satisfy evolving demands from customers, AWS focused on technology innovation, global expansion, and key partnerships while maintaining its leadership position in the market.
2021 : Amazon maintained its position as the industry's top cloud provider by promoting user adoption, environmental efforts, and R&D spending.
2022 : As it continued to service millions of clients globally, AWS maintained its position as the industry leader in cloud computing, leading initiatives for growth, innovation, and responsibility.
AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS is a global cloud computing platform that is accessible from any location.
It operates in various parts of the world since it has a global infrastructure.
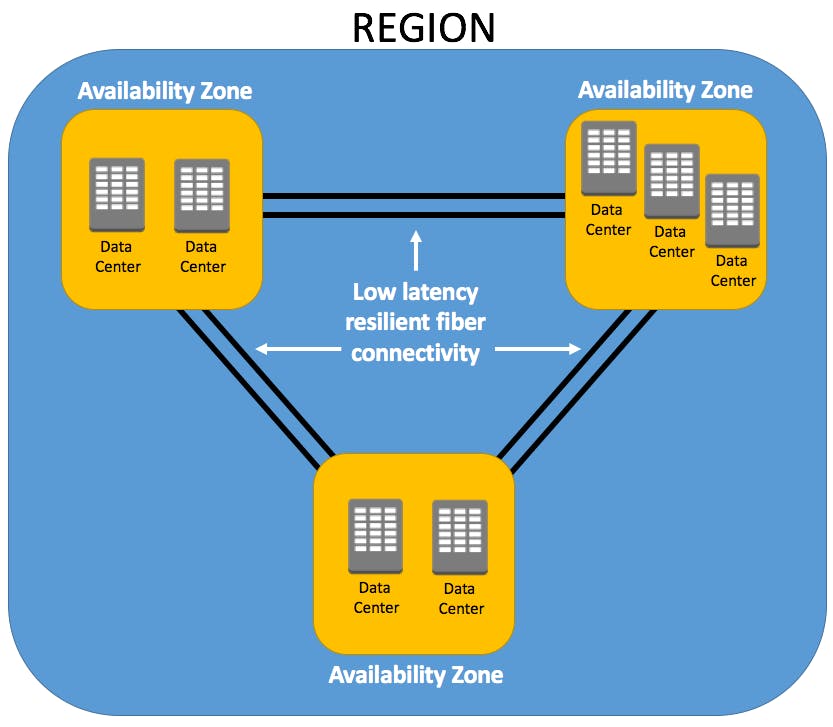
There are several availability zones basically, separate data centers in each region.
By 2024, AWS will be present in over 80 availability zones spread throughout 25 different worldwide geographic regions. Businesses can proactively put their apps and services in these zones, guaranteeing immediate delivery of optimal performance and dependability to end customers.
Several essential elements of the AWS infrastructure are developed to guarantee dependability and speed:
Region
Availability Zones
Edge Locations
Regional Edge Caches
Region
What is a Region ?
An AWS region is a specific geographic location that contains AWS data centers.
Every Region is separate and functions independently of all the others.
Why are Regions important ?
You can select the actual location of your resources, such as servers and databases, using regions.
They allow you to put resources in close reach to your users, which improves performance and meets with local regulations.
Key Points :
To provide redundancy and fault tolerance, each Region consists of numerous Availability Zones (AZs).
The functionality and availability of AWS services may vary based on the region.
Descriptive names are used to identify regions, such as ap-south-1 (Mumbai) or eu-west-1 (Ireland) or us-east-1 (Virginia).
Usage :
To cut down on latency and boost efficiency, you can choose the Region that is nearest to your users.
Companies that operate internationally can use several Regions to guarantee disaster recovery and high availability.
Scenario :
Assume you run an internet-based clothing business with clients all around the world. No matter where someone is, you want your website to load quickly for them.
Should you choose to host your website on AWS, you can choose between hosting it in the US (Virginia) or Europe (Ireland).
The data from your website will be kept in AWS data centers located on the east coast of the United States if you select US (Virginia).
Your website's data will be kept in AWS data centers located in Ireland if you select Europe (Ireland).
Here's why Regions matter :
Speed : Locating your website in Europe that is, Ireland can help it load faster for your clients if the majority of them are in Europe, as less data will need to go there.
Reliability : In the event of an issue in one Region such as bad weather or a power outage your website can continue to function from the other Region.
Compliance : There are laws in several nations governing the storage of data. You may ensure that your website follows with those guidelines by selecting the right Region.
So, wherever your clients may be, you can ensure that your online store operates quickly, consistently, and legally by selecting the appropriate AWS Region.
Availability Zones
What are Availability Zones (AZs) ?
AWS's data centers are situated in remote areas known as Availability Zones (AZs).
Although they are linked by low-latency networks, each AZ functions independently of the others.
Why are they important ?
AZs offer fault tolerance and redundancy. High availability is ensured by the fact that if one AZ fails, the others keep running.
They let you spread out the deployment of your apps across multiple locations for increased dependability.
Key Points :
To keep things running even in the event of a failure, each AZ has its own power, cooling, and networking systems.
They are built to resist interruptions and natural disasters.
You can reduce the impact of localized failures on your applications by allocating resources among AZs.
Usage :
A highly available and fault-tolerant architecture can be created by deploying your infrastructure such as databases, storage, and EC2 instances across many AZs.
For enhanced stability, AWS services like Amazon RDS, Amazon S3, and Amazon EC2 are made to function smoothly across AZs.
Scenario :
Assume you have an international user base for your AWS-powered website. In order to ensure that it is always available, you configure it in two distinct locations known as "Availability Zones." These areas resemble different rooms inside the same structure.
Here's how Availability Zones come into play :
Redundancy : You can guarantee reliability by deploying your application across multiple availability zones (AZs). The program can function smoothly from the servers in the other AZ even in the event of a hardware malfunction, power outage, or other problem impacting one AZ.
Fault Tolerance : Imagine an unexpected spike in traffic that overwhelms one AZ's servers, making them slow or unresponsive. Your users will always have service since the load balancer can automatically reroute traffic to the servers in the other AZ.
Disaster Recovery : The application can failover to the servers in the unaffected AZ in the event of a natural disaster or other catastrophic event that affects one AZ, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Low Latency : AZs have low latency connections since they are nearby but physically apart. This implies that there will be little delay for customers who are using your application from different geographical locations.
Multiple Availability Zones are used to ensure that the website always remains up and operates quickly.
Edge Locations
What are Edge Locations ?
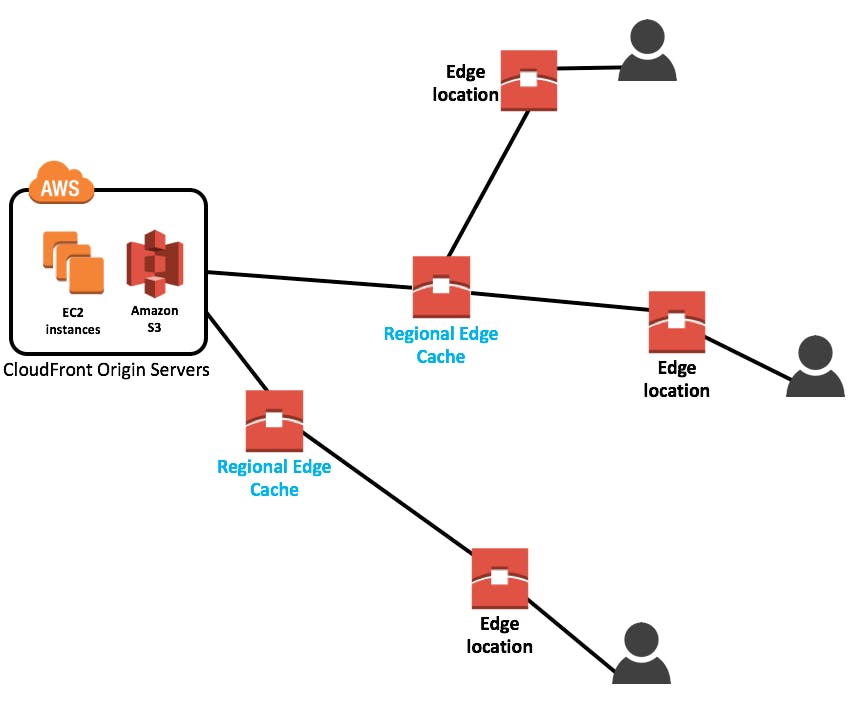
- Amazon CloudFront, AWS's content delivery network (CDN), keeps copies of your data in locations known as Edge Locations.
Why are they important ?
- Edge Locations are placed in key locations across the globe to improve speed and lower latency by bringing content closer to users.
Key Points :
Edge Locations are smaller facilities situated in significant cities and regions; they are not data centers.
To provide users with fast access to commonly visited content, such as photographs, movies, and web pages, they keep copies of such materials.
Usage :
- CloudFront speeds up page loads by delivering material from the closest Edge Location to the user who wants it from your website or application.
Benefits :
Faster content delivery : Users benefit from improved performance and faster load times.
Scalability : Edge Locations adjust automatically to demand and traffic variations.
Global reach : Your content may reach viewers in remote places without compromising speed thanks to Edge Locations worldwide.
Scenario :
Assume you have an online gallery-style website with a large number of images and videos. Viewers come to your site from all over the world to see these pictures and videos.
Rather than keeping all of your photos and videos in one location, AWS distributes them around numerous locations known as "Edge Locations." These can be thought of as small storage rooms distributed around various global cities.
Suppose someone from Tokyo requests to view a photo on your website. Rather than obtaining that image from a distant server, it is already saved in a nearby Edge Location. As a result, the image loads practically immediately.
Now, a visitor from New York want to view a video on your website. Once more, the video is saved at an Edge Location near them, so there is no waiting for it to begin playing.
No matter where they are, these Edge Locations speed up the loading of your website for everyone. It's like having duplicates of your photos and films spread out throughout storage facilities, waiting to be instantaneously accessed by anyone who requests them.
Regional Edge Cache
What is a Regional Edge Cache ?
One kind of caching node that is situated near customers at the edge of AWS's network is called a Regional Edge Cache.
It keeps commonly accessed material in the AWS network at a more regional level.
This is not the same as Edge Locations, which are mostly concerned with content caching on a smaller, city-level scale.
Why are they important ?
In order to minimize latency and enhance performance, frequently accessed content is stored closer to users through the smart placement of both Regional Edge Caches and Edge Locations.
Regional Edge Caches expand this caching capacity to a larger regional level inside the AWS network, whereas Edge Locations are primarily focused on caching material at a smaller, city-level scale.
Usage :
Content is supplied to users via Amazon CloudFront from Edge Locations, where it is cached according to popularity and user demand.
In addition to Edge Locations, Regional Edge Caches enhance content delivery and lower latency for users by caching content at a greater scale within the same region.
Scenario :
Assume you run a well-known website for streaming videos that is hosted on AWS. Visitors to your website to watch videos come from all over the world.
When a user in New York requests to watch a popular video :
First, the Regional Edge Cache in the US East (Virginia) area receives the request.
If the video is already saved close by, the Regional Edge Cache looks for it.
The user in New York receives the video fast if it is cached in the Regional Edge Cache, which minimizes buffering and offers an uninterrupted viewing experience.
The request is sent to the closest Edge Location in New York City if the video is not cached in the Regional Edge Cache.
A user in London now makes a request for the same video:
The request is sent to the Regional Edge Cache in the EU (Ireland) region rather than the US origin server in order to get the video.
If the video is already saved close by, the Regional Edge Cache looks for it.
A smooth viewing experience is ensured and latency is reduced when the viewer in London receives the movie promptly if it is cached in the EU region Regional Edge Cache.
The request is sent to the closest Edge Location in London if the video is not cached in the Regional Edge Cache.
In order to further optimize content delivery and lower latency, the request is then forwarded to the closest Edge Location in all scenarios if the video is not stored in the Regional Edge Cache.
Conclusion
AWS's Evolution : Amazon is now a major cloud computing provider. It is concerned with maintaining the environment, creating new products, and satisfying customers.
Flexibility and Affordability : Businesses may easily adjust how much they use with AWS and don't have to pay a large upfront cost. They can try new things and save money thanks to this.
Reliability and Security : AWS specializes at maintaining system functionality and guaranteeing data security. They have powerful computers and data protection policies.
Global Reach and Performance : Amazon helps companies make their products available to everyone. It ensures that operations run smoothly and that various locations follow to the guidelines.
