Introduction to Cloud Computing
The Evolution of IT: From On-Premises to the Cloud
Introduction
Definition
Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access computer services such as storage, processing power, and software over the internet without requiring any physical infrastructure ownership.
Concept
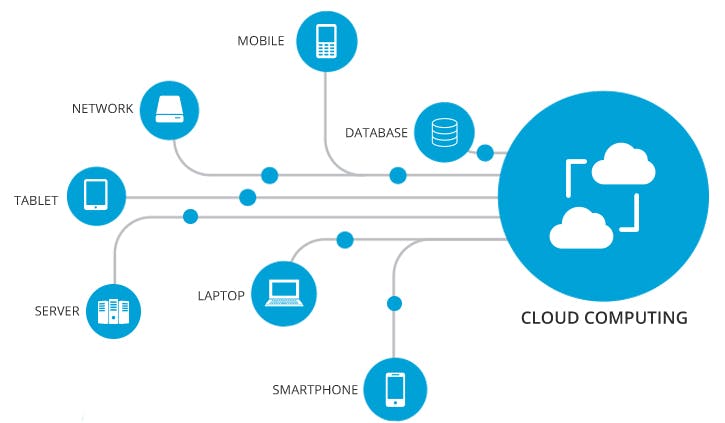
Remote Access : Users no longer need to save data and programs on a local server or personal computer because they can access them remotely over the internet thanks to cloud computing.
On-Demand Services : Users of cloud services can scale resources up or down in accordance with their demands because they are usually offered on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis.
Shared Infrastructure : In order to maximize resource utilization and cost effectiveness, cloud providers operate sizable data centers with powerful servers and storage systems that are shared by numerous users.
Virtualization : Virtualization is a common technique used in cloud computing to generate virtualized versions of computing resources, which are more manageable and flexible.
Accessibility : Users can use a range of devices, including as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, to access cloud services from any location with an internet connection.
Scalability : Businesses can easily add or remove resources to quickly adapt to changing needs thanks to the amazing scalability of cloud services.
History
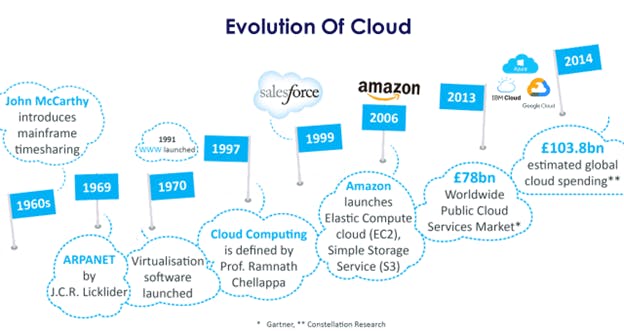
Time-sharing and remote access to mainframe computers emerged in the 1960s and 1970s, which is when the idea of cloud computing first emerged.
Cloud computing principles were first established through the exploration of ways by which researchers and developers may effectively distribute computing resources across several users.
Application Service Providers (ASPs) started providing subscription-based online access to business software and applications in the 1990s.
An early kind of cloud computing existed at this time, allowing users to access software remotely without having to install anything locally.
Businesses such as Amazon and Salesforce began providing Software as a Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in the early 2000s.
Modern cloud architecture was founded around the concept of on-demand virtual server and storage space rentals, which was first introduced by Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2002.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) was released by Google App Engine (2008) and Microsoft Azure (2010), giving developers the tools and frameworks they need to create and launch cloud-based applications.
A large portion of the foundational infrastructure was taken away by these platform services, allowing developers to concentrate on developing applications rather than managing servers.
In the 2010s, cloud computing became widely used in many industries due to technological breakthroughs, cost-effectiveness, and scalability.
In order to increase performance and dependability, cloud providers kept innovating by launching new services like serverless computing (also known as Function as a Service) and growing their global infrastructure.
Modern IT infrastructure now cannot function without cloud computing, which powers everything from big data analytics and artificial intelligence to e-commerce platforms.
In order to meet changing possibilities and challenges, cloud computing is expected to become even more integrated with cutting-edge technologies like edge computing, quantum computing, and advanced safety features in the future.
Importance & Benefits
Importance
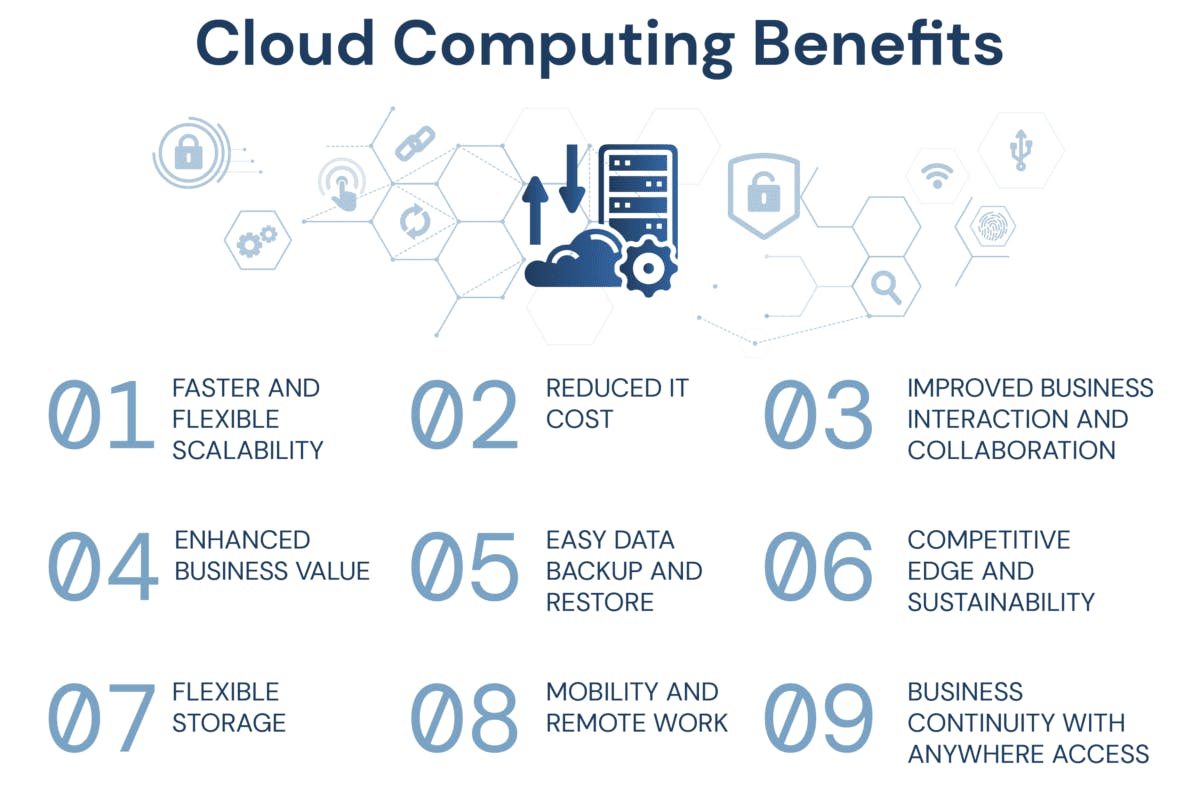
Digital Transformation : The ability to access scalable and affordable IT resources is a key feature of cloud computing, which helps organizations undergo digital transformation.
Innovation Accelerator : By giving developers and companies the resources they need to swiftly build and implement new apps, it promotes innovation.
Global Connectivity : Businesses can communicate with clients anywhere in the globe with cloud computing, eliminating the need for localized physical infrastructure.
Economic Growth : The adoption of cloud computing boosts economic growth by reducing startup entry barriers and increasing productivity across industries.
Benefits
Scalability : Cloud services are effective at managing variations in workload because they can quickly modify resources in response to demand.
Cost Efficiency : Expect predictable prices as a result of cloud computing's flexible payment plans and lower upfront hardware expenditures.
Flexibility and Agility : Businesses may experiment with innovative technologies, launch new apps, and react quickly to shifting market conditions thanks to cloud computing, which eliminates the need for standard IT configurations.
Accessibility : Cloud services enable smooth collaboration and remote work since they are accessible from any location with an internet connection.
Security and Reliability : Compared to on-premises systems, top cloud providers invest in security measures to ensure data safety and dependability.
Conclusion
A lot has happened in cloud computing since the 1960s. From beginnings that started as basic services, it has grown to be essential to developers and enterprises.
Cloud computing has transformed how companies operate. They develop and generate new ideas as a result of it. It acts as an accelerator for global economic growth and enables international business-related relationships.
Accessing cloud computing is simple. If you have internet access, you can work from anyplace. Businesses can move quickly and efficiently with its assistance.
In addition to being secure, cloud computing saves money. It is less expensive than making large upfront hardware purchases. People trust it because it is trustworthy and secures data.
Cloud computing will continue to advance. Modern technology such as edge and quantum computing will function with it. It will become even safer. Therefore, it will continue to be essential for innovation, development, and smaller the world.
