Introduction to Linux Operating System
Getting Started with Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Introduction
Linux is a free and open-source operating system and it's available to everyone without any cost.
It works on a core called the Linux kernel, which handles basic computer functions such as memory and hardware.
Different versions of Linux, called "distros," bundle the Linux kernel with various software to create complete operating systems suited to different needs.
Linux is well-known for being stable, secure, and scalable, making it popular for many types of devices, including servers, desktops, and mobile devices.
Linux supports a wide range of software applications, like web servers, office suites, and multimedia players, often available through simple installation systems.

History and Evolution of Linux
Origins in Unix :
Linux has its origins in the Unix operating system, which was created by AT&T Bell Labs in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
Unix became popular in academic and research institutions because of its powerful features and flexibility.
Birth of Linux :
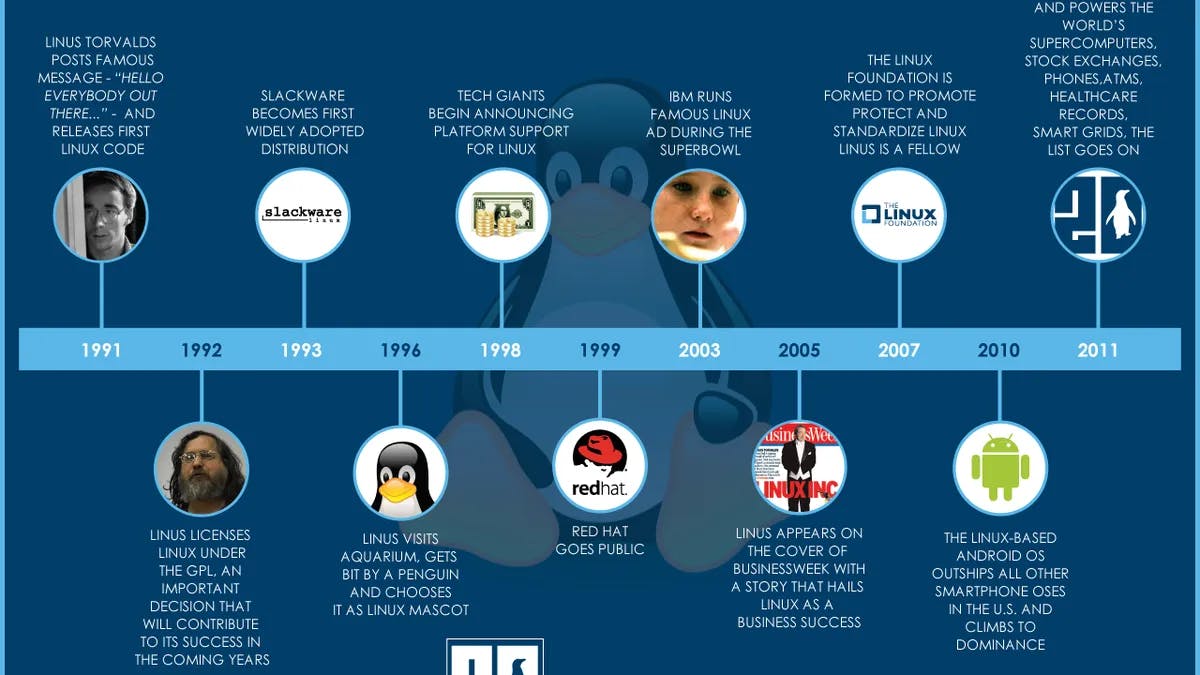
In 1991, Linus Torvalds, a Finnish computer science student, created the Linux kernel as a personal project.
On September 17, 1991, Torvalds publicly released the first version of the Linux kernel, known as version 0.01. He made it freely available under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
Rapid Growth and Collaboration :
Linux rapidly attracted developers from around the globe, who actively contributed to its growth and improvement.
The open-source nature of Linux fosters collaboration among programmers, which leads to quick advancements and bug fixes.
The Rise of Linux Distribution :
As Linux became more popular, various distributions (often called distros) emerged, each with its unique package management system and user interface.
Early notable distributions include Slackware (1993), Debian (1993), and Red Hat Linux (1994), which set the stage for the diverse array of Linux distributions we have today.
Enterprise Adoption and Expansion :
Throughout the 2000s, Linux became increasingly popular in enterprise environments due to its stability, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Major corporations like IBM, Oracle, and Red Hat started providing enterprise-grade Linux distributions along with support services.
Presence in Computing :
Linux is now found in almost every type of technology, from powerful servers and supercomputers to everyday smartphones, smart devices, and embedded systems.
Android, the world's most popular mobile operating system, is based on the Linux kernel.
Continued Innovation and Community Growth :
The Linux community continues to grow, with thousands of developers contributing to the kernel and various open-source projects.
Linux continues to lead the way in technological innovation, with ongoing efforts focusing on areas like cloud computing, containerization, and artificial intelligence.
Linux Distribution
Linux distributions, known as "distros," are variations of the Linux operating system. There are hundreds available, like
Ubuntu
Fedora Linux
Linux Mint
Manjaro
Debian , and many more

Difference between Unix and Linux
| Aspect | Unix | Linux |
| Licensing | Typically, you need to buy a license for business use. | Open-source, freely available |
| Kernel | Usually operates on its own specialized core system. | Based on the Linux kernel, open-source and customizable |
| File System | Often uses UFS or ZFS | Commonly uses ext4, XFS, or Btrfs |
| Development Community | Community support may be limited | Active community providing help and improvements. |
| Compatibility and Portability | Closely tied to certain hardware setups and platforms. | Highly portable, runs on various hardware architectures |
| Support and Documentation | Vendors offer extensive support and documentation. | Support options vary by distribution. |
Conclusion
Linux has evolved into a trusted operating system renowned for its stability, security, and adaptability, serving users globally.
Linux plays a crucial role in the IT industry thanks to its cooperative development, which is fueled by open-source principles and guarantees continual advancements and innovative ideas.
Users can quickly identify a Linux version that meets their requirements by selecting from a range of versions that provide easy customization and simple user experiences.
Linux is available to everyone and offers powerful hardware at affordable prices thanks to its open licensing and flexibility. Beginners, companies, and enthusiasts can all benefit from it.
Linux is a popular option for a variety of computing demands, even for those who are new to technology because it operates on a variety of devices and provides simple integration.
