Table of contents
Introduction
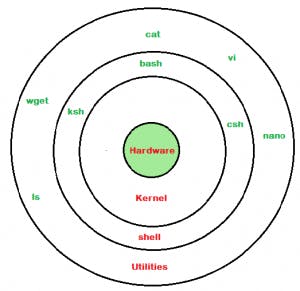
Linux architecture has the following components :
Kernel :
An operating system based on Linux is controlled by its kernel.
It arranges and monitors the utilization of the computer's fundamental components, such as memory and processing capacity.
The kernel makes sure that various programs don't clash or interfere with one another.
It manages the communication between the computer and devices such as network connections, printers, and keyboards.
Programs can save data, connect to the internet, and display content on the screen with the help of the kernel.
It improves program memory management and helps the computer remember where its resources are stored in memory.
C is usually used to write the kernel of an operating system that runs on Linux.
Shell :
The Linux operating system's shell functions similarly to a talking point.
By inputting commands into the shell, users can communicate with the system.
These commands are understood by the shell, which carries out user requests.
It connects users to the kernel, the central component of the system.
The shell assists in bridging the gap between the language the kernel knows and human language, which is written in C.
The shell receives instructions from users and sends them to the kernel.
Users may easily launch programs, organize files, and configure the system with the help of the shell.
Users can select the shell that best fits their needs and workflow by selecting from a variety of features and capabilities offered by several shells, including Fish, Zsh, and Bash.
One of the most popular shells, bash, is a superset of the more feature-rich and traditional "sh" (Bourne Shell) shell.
System Library :
System libraries, sometimes referred to as shared libraries, are what enable Linux to function as an operating system.
System libraries serve as a bridge between the operating system's kernel, which powers programs, and other applications.
Programs can use the ready-made code found in these libraries to do particular tasks.
For programs to interact with the underlying system, they offer a standardized and effective method.
Using these libraries saves developers time and effort since they eliminate the need to write the same code repeatedly.
The Linux community continuously updates and maintains system libraries, guaranteeing system security and stability.
Hardware :
At the bottom of the operating system track is where Linux's hardware layer functions.
It is essential to the management of every piece of hardware.
This layer includes:
Device drivers
Kernel functions
Memory management
CPU control
I/O operations
Its primary purpose is to reduce hardware complexity.
The hardware layer makes sure that every part functions as it should.
Application / System Utility :
In Linux, system utilities are crucial applications and tools.
These tools can monitor system performance, configure networks, and install applications.
They provide the configuration and management of various system components.
Users can more easily and effectively maintain their Linux systems with the help of system utilities.
They also take care of things like user management and access control.
In addition, system utilities include instruments for tracking down problems with the system, like examining system logs and identifying hardware malfunctions.
Conclusion
The essential elements of the Linux architecture, in brief, are as follows:
Kernel : It manages resources and ensures that everything functions properly and safely, acting as Linux's brain.
Shell : This is the way that you communicate with Linux. It follows your instructions and completes the task at hand. It functions similarly to a useful helper for your computer-related duties.
System Library : These resemble program toolkits. They simplify software's interaction with the CPU, saving developers from having to create everything from scratch each time.
Hardware : These are the hardware components of your computer, such as the keyboard and RAM. Linux is skilled at making efficient use of them to accomplish your goals.
Application/System Utility : These are useful programs that assist you with computer management. They do tasks like network configuration, software installation, and system monitoring.
These parts are comparable to Linux's fundamental parts. Together, they ensure that your computer performs well for a variety of tasks.
