Types of Cloud Computing
The Evolution of IT: From On-Premises to the Cloud
Introduction
A new technology called cloud computing has changed the way we handle, store, and use data.
It means getting computing resources—such as storage, servers, and software—through the Internet.
Your data is saved on computers that are connected to the Internet, not on physical devices.
Cloud service providers use advanced safety features to protect your information.
They make use of virtual walls (firewalls), secret codes (encryption), and rules (access limits).
Even if your own gadgets are misplaced or malfunction, your data remains secure.
Cloud services maintain backup copies of your data in case something goes wrong.
If something goes wrong, these copies, or backups, make it easy and quick to restore your data.
Types of Cloud
There are five main sorts of clouds that you might use, depending on what your business needs.

Public Cloud
Anyone can use it to save and retrieve information via the internet.
Under the direction and control of the cloud service provider (CSP).
The CSP maintains the infrastructure and guarantees the scalability and accessibility of resources.
It is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of location or size of business.
Users are able to run apps, save data, and access a variety of services.
Customers only pay for what they use because it uses a pay-per-usage model, which is economical.
Examples include Microsoft, IBM SmartCloud Enterprise, Google App Engine, Windows Azure Services Platform, and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
Characteristics of Public Cloud
Programs and data are accessible to anybody with internet access, anywhere, at any time. Because so many people share them, money and resources are saved.
It is quick and easy for users to switch between resources without having to pay for them up advance.
Providers maintain the technology, ensuring that security and backups function properly.
They also use powerful locks, such as encryption, and routinely check to keep things safe.
Advantages of Public Cloud
When compared to private and hybrid clouds, public clouds are more affordable.
The cloud service provider takes care of maintenance, so there are no concerns for the user.
It provides users with flexibility and simple integration.
It is location-independent and available via the internet from any location.
Highly scalable to changes in computational power requirements.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
The shared resources that are available to the public may make public clouds less secure.
A good internet connection to the cloud provider is necessary for optimal performance.
Since the supplier is in charge of managing their data, users have less control over it.
The availability and service agreements of the supplier determine reliability.
It may be difficult to fulfill the rules if you don't follow industry standards and guidelines.
Private Cloud
Organizations use private cloud, sometimes referred to as internal or corporate cloud, to set up and manage their own data centers.
Private clouds can be implemented by businesses either within the company or by using third-party providers.
When creating private clouds, opensource technologies like Eucalyptus and Openstack are frequently utilized.
OpenStack, Microsoft Azure Stack, Oracle Cloud at Customer, IBM Cloud Private, and VMware vSphere are a few examples.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) splits private cloud into the following two categories based on management and location:
On-premise private cloud :
Located within the physical infrastructure of the organization.
Maintains a specialized data center with cloud services available only for internal usage.
Organizational control over the configuration and customization of the infrastructure remains unchanged.
Enables efficient handling of security and regulatory issues.
Requires expensive setup and management costs in terms of software, hardware, and IT skills.
Outsourced private cloud :
Involves hosting and managing the cloud infrastructure in collaboration with a third-party service provider.
The private cloud may be operated by the provider out of their own data center or at a shared location with several businesses.
Organization gains from the resources and experience of the supplier, which reduces the difficulty of managing the infrastructure.
Scalability is provided by the provider, who can modify resources based on the requirements of the enterprise.
Perfect for companies looking to benefit from private cloud features without having to pay for initial setup fees or continuous maintenance.
Businesses have more control over their data, apps, and security with both on-premise and managed private clouds as compared to public cloud choices. Organizations with strict guidelines, sensitive data, or specialized workloads needing high levels of customisation and security are particularly suitable for private clouds.
Characteristics of Private Cloud
Private cloud services are restricted to one company, guaranteeing unique resources and services. It is similar to having a private cloud environment set aside just for that company.
Organizations now have more security and control over information management and access control.
Organizations can set resources for best performance thanks to the wide customization options offered by private clouds.
Private clouds provide effective resource use because they are built for smooth resource allocation and growth.
Private clouds enable rules with regulatory standards and give improved reliability with direct control over infrastructure.
Organizations are able to take use of the advantages of both environments thanks to the easy integration of private clouds with public cloud services.
Advantages of Private Cloud
Sensitive data is protected by the high security and privacy provided by private clouds.
It offers more storage capacity and enhanced performance at quicker speeds.
Businesses don't rely on outside parties because they have total control of their cloud.
Adjustable to satisfy specific legal and business needs.
In order to guarantee continuous operations, private clouds offer higher reliability and smooth interaction with current systems and apps.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
Managing cloud services requires management from qualified experts.
Private cloud services are limited in scope by internal organization restrictions.
Suitable not for large user bases or enterprises without proper infrastructure or maintenance staff.
Higher up-front and continuing maintenance costs are associated with private cloud.
When considering options for public or hybrid clouds, scaling resources might be more difficult.

Hybrid Cloud
A flexible computing environment is produced via hybrid cloud computing, which integrates parts of private and public cloud configurations.
Hybrid cloud is only partially safe because private cloud services are only available to customers within the company, but public cloud services are available to everybody.
Both public and private clouds offer benefits to organizations, including scalability and flexibility.
In a hybrid cloud configuration, public cloud services from outside providers are reachable via the Internet.
Organizations can increase the flexibility and scalability of their computing resources by bringing together public and private clouds.
Examples include Office 365 (MS Office on the Web and One Drive), Amazon Web Services, and the Google Application Suite (Gmail, Google Apps, and Google Drive).
Characteristics of Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud infrastructure to provide a single area for workload and data management.
Businesses are able to easily modify their resources, adding public cloud services to their private cloud to allow for scale without sacrificing control.
Control over critical data and apps is ensured by hybrid cloud, which combines the flexibility of public clouds with the security of private clouds.
Costs can be minimized by managing resources across public and private clouds effectively, with private clouds being used for workloads that are crucial and public clouds for less important ones.
The hybrid cloud makes it possible to move apps and data between public and private clouds without interruption, to implement rules and laws, and to adjust to changing requirements.
The risk of data loss or service interruptions is reduced when essential data and applications are copied between private and public clouds, improving disaster recovery and enterprise continuity plans.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
Organizations with higher security requirements might consider hybrid cloud since it provides more security than public cloud.
Businesses can improve company flexibility by launching new products and services more quickly using hybrid cloud.
By using hybrid cloud, operations and data management risks can be decreased.
The hybrid cloud offers resource utilization flexibility by combining safe private cloud resources with adaptable public cloud resources.
Operations can be improved by using hybrid cloud to enable smooth integration between on-premises infrastructure and cloud setups.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
Even though hybrid cloud is more secure than public cloud, private cloud security may still be superior.
Taking care of several deployment models at once makes managing a hybrid cloud difficult.
The performance of cloud service providers determines the availability of a hybrid cloud's services are.
It can be difficult to integrate data and guarantee smooth connectivity between several cloud systems.
Compared to single-cloud solutions, managing and integrating numerous cloud environments may result in higher expenses.
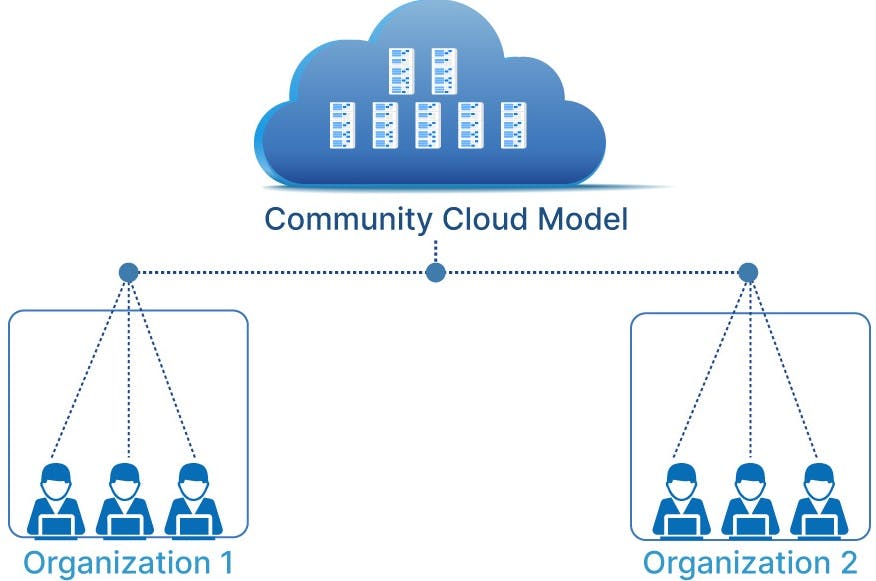
Community Cloud
A community cloud promotes cooperation and information sharing by giving several organizations in that community access to common systems and services.
One or more community organizations, a third party, or a combination of them own, manage, and run it.
The participating organizations work together to create a shared cloud architecture that enables the use of common data, applications, and services.
Collaborating to create a community cloud with services customized to each member's needs, organizations within the same industry, government, or other community work together.
Access to shared services, apps, and data relevant to the community's member organizations is made possible by community clouds.
Examples include government (FedRAMP), banking (PCI DSS), and healthcare (HIPAA compliance).
Characteristics of Community Cloud
A community cloud provides a shared computing environment that effectively meets the demands of a particular group of businesses.
The community cloud's services and resources are customized to each participating organization's unique needs, allowing rapid communication and teamwork.
The community cloud, which is either third-party or community-managed, guarantees governance that is in line with common goals.
Strong security protocols and legal structures designed to meet local regulatory requirements are given top priority by community clouds.
Organizations may reduce their financial burden through cost sharing, which increases the affordability and sustainability of cloud adoption for all parties involved.
Advantages of Community Cloud
Community cloud is an affordable solution because it allows multiple enterprises to share the complete cloud infrastructure.
Organizations that place a high priority on data protection might consider the community cloud since it offers superior security measures than the public cloud.
It promotes efficiency and teamwork by encouraging cooperation and resource sharing amongst involved entities.
The usage of resources is improved when several businesses may share cloud resources, infrastructure, and capabilities thanks to community cloud.
Sharing security measures make it easier to keep up with industry requirements while providing customisation choices to fit the specific demands of the community.
Disadvantages of Community Cloud
Some organizations may not find community cloud appropriate because of particular limitations and needs.
Community clouds may not have the same level of protection as private cloud systems, but having better security than public clouds.
The success of a community cloud deployment depends on community members working together.
All community members share fixed data storage and bandwidth, which could cause resource competition and performance problems.
As the community cloud's capacity relies on shared resources, its capacity to satisfy increasing demands may be limited and cause scalability issues.
Multi-Cloud
Using public, private, and hybrid clouds as well as other cloud service providers and platforms to meet computing needs is known as a multi-cloud strategy.
In order to maximize flexibility and performance, businesses distribute workloads, apps, and data throughout many cloud environments.
Using a multi-cloud strategy gives companies the flexibility to select and make use of the best cloud services available from many providers, meeting their unique requirements.
Businesses can minimize the danger of vendor lock-in and take advantage of the distinct features and services provided by each cloud provider by spreading their sources.
Using a multi-cloud strategy maximizes cost-effectiveness and resource usage by enabling firms to take advantage of competitive pricing models provided by various cloud providers.
AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are a few examples.
Characteristics of Multi-Cloud
Using many providers for a variety of services, such as AWS, Azure, and GCP, is known as multi-clouding.
Spreading out workloads among several clouds reduces the effect of service interruptions and vendor lock-in.
Based on their requirements, businesses can choose the best services from several sources, reducing dependence on a single supplier.
By selecting the most economical supplier for every task, taking advantage of specialist services and affordable prices, organizations can minimize expenses.
Multi-cloud computing utilizes resources from several providers to increase performance, scalability, and dependability.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud
Organizations can select the best cloud services from several providers according to their unique requirements thanks to multi-cloud.
The distribution of workloads and data among many cloud environments enhances dependability and guarantees durability in the event of service interruptions or unavailability.
Organizations can reduce the danger of vendor lock-in and avoid relying completely on one vendor by using a variety of sources.
By choosing the most affordable cloud provider for each workload or application, organizations are able to optimize both costs and services.
By integrating infrastructure and resources from many cloud providers, enterprises can attain enhanced performance, scalability, and high availability.
Disadvantages of Multi-Cloud
Several cloud environments might be difficult and complex to manage.
Multiple subscriptions and data transfer fees between various cloud providers could come at a larger cost.
It becomes increasingly difficult to ensure data management and security while using several clouds.
It can be difficult to integrate and guarantee integration amongst various cloud providers.
Managing several cloud environments may result in higher resource requirements and management complexity.

Conclusion
Numerous alternatives, including public, private, hybrid, community, and multi-cloud, are available with cloud computing.
When using cloud computing, security, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility are important factors.
The efficiency of operations is improved through cooperation and resource sharing.
For cloud installation to be effective, strategic planning is essential.
Optimizing cloud benefits requires effective risk prevention and alignment with company goals.
